RPA automation is changing the way businesses handle repetitive, rule-based tasks, letting people focus on more important work. When combined with AI in ITSM – ITSM에서의 AI – and AI solutions for contact centers, it becomes a powerful tool for faster, more accurate, and scalable operations.
Today, cloud-based AI is helping companies run smarter and more flexible systems without needing heavy on-site infrastructure. Modern computer technologies make it easier to automate tasks and use data to make better decisions. AI in marketing is helping businesses reach the right audience with personalized messages, while digital marketing powered by AI makes campaigns more efficient and results easier to track.
In finance, AI is speeding up processes like fraud detection, reporting, and risk management, making operations safer and more accurate. Together, these tools create a smooth system where RPA automation drives efficiency, AI adds intelligence, and digital tools help businesses grow.
This guide will show you what RPA automation is, how it works, the benefits you can get, and how to create a practical roadmap for success.
Top Contact Center Solutions Using RPA Automation to Boost Efficiency and Customer Experience
When it comes to improving customer support, increasing productivity, and streamlining operations, RPA automation is now a key tool for contact centers. Integrating AI into contact center solutions allows businesses to handle routine tasks automatically while agents focus on higher-value interactions. Here’s a list of top platforms transforming contact centers today:
1. Bright Pattern – Leading RPA and AI-Powered Contact Center Solutions
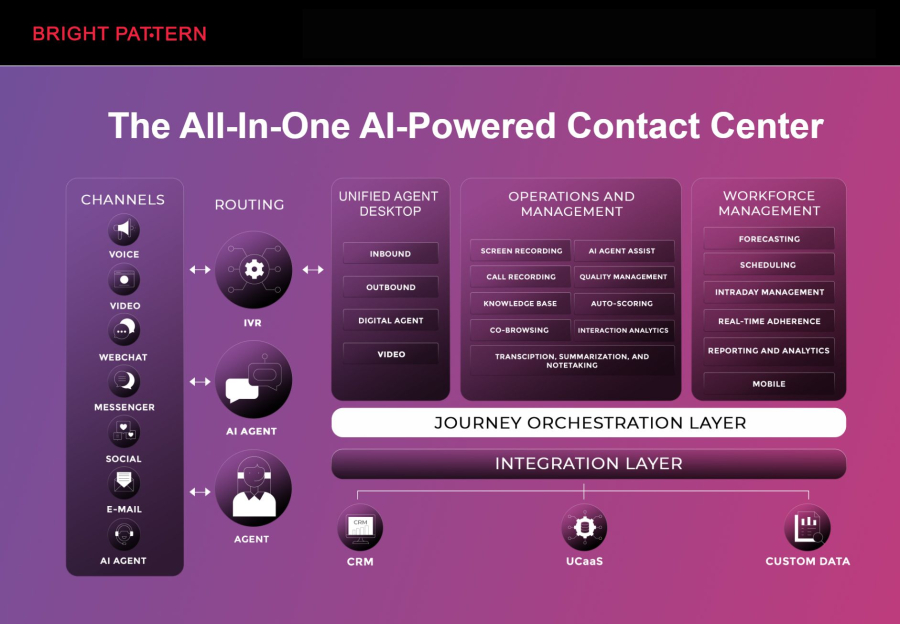
Bright Pattern is a leading platform that combines RPA automation with AI solutions for contact centers, helping businesses deliver seamless customer experiences across multiple channels. Its intuitive design makes it easy to integrate with ITSM tools and other enterprise systems.
Key Features:
- Omnichannel support – manage calls, chat, email, and social media from one platform
- AI-powered routing – automatically direct customers to the right agent or solution
- RPA automation for repetitive tasks – streamline data entry, ticket updates, and follow-ups
- Analytics and reporting – gain insights to optimize performance and customer satisfaction
- Cloud-based flexibility – scale operations without heavy infrastructure costs
Bright Pattern’s combination of RPA and AI in contact centers allows companies to reduce response times, improve agent efficiency, and create a more personalized customer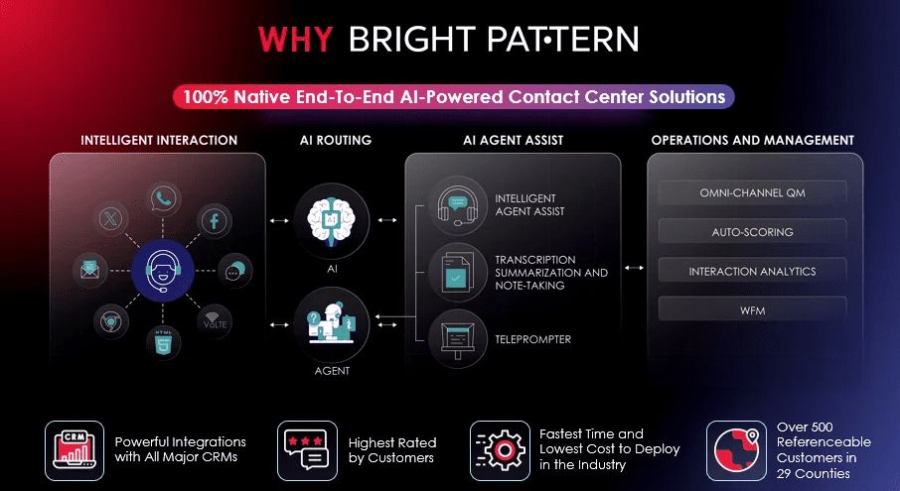 experience.
experience.
2. Five9 – Cloud Contact Center with Intelligent Automation
Five9 offers cloud-based contact center software with AI-driven automation to optimize agent performance and customer interactions.
3. Genesys Cloud – AI-Enhanced Customer Experience Platform
Genesys Cloud integrates AI and automation to deliver seamless omnichannel experiences and predictive analytics for better customer service.
4. NICE inContact – Advanced Contact Center Solutions
NICE inContact uses AI to improve agent workflows, automate routine tasks, and provide detailed analytics for business insights.
5. Talkdesk – AI-Driven Cloud Contact Center
Talkdesk combines RPA automation with AI to enhance call routing, reduce wait times, and improve agent productivity.
6. 8x8 Contact Center – Unified Communications and Automation
8x8 offers AI-powered automation for customer engagement across voice, chat, and social media channels.
7. RingCentral Contact Center – Intelligent RPA Solutions
RingCentral integrates RPA and AI to simplify workflows, automate repetitive processes, and enhance agent performance.
8. Cisco Contact Center – Scalable AI-Powered Platform
Cisco provides AI-driven tools for task automation, predictive routing, and omnichannel customer support.
9. Vonage Contact Center – AI and Automation Combined
Vonage offers AI-enabled automation to improve customer experience, streamline repetitive tasks, and enhance team efficiency.
10. Zendesk – AI Solutions for Smarter Customer Service
Zendesk integrates AI and automation tools to manage tickets, analyze customer interactions, and optimize support workflows.
What Is RPA Automation?
Robotic Process Automation(RPA) is a technology that uses software robots, orbots, to mimic the way a human interacts with digital systems. These bots click, type, copy, paste, read screens, and move data between applications in the same way a person would, but faster and without getting tired or distracted.
RPA automation is best suited for processes that are:
- Rule based: The steps follow clear, pre‑defined rules.
- Repetitive: The same actions are performed over and over.
- High volume: Many transactions or cases per day, week, or month.
- Digital: The process uses structured data and standard applications.
Think of RPA as a virtual workforce that handles the tedious, time‑consuming tasks, while your people focus on customers, innovation, and strategic work.
How RPA Automation Works
Although tools differ, most RPA platforms share a similar set of components and a common way of working.
Core Components of RPA Automation
- Software robots: The scripts or bot programs that execute tasks according to defined rules.
- Process recorder or designer: A visual tool where you map steps, drag‑and‑drop actions, or record user interactions to create a workflow.
- Orchestrator or control center: The console used to deploy, schedule, monitor, and manage bots across systems and environments.
- Connectors and integrations: Pre‑built components that connect bots to enterprise systems such as CRM, ERP, email, and databases.
Typical RPA Automation Lifecycle
- Identify a process: Select a suitable, rules‑based process with clear business value.
- Document the workflow: Capture each step, decision rule, input, and output.
- Design and build the bot: Use the RPA tool to replicate the workflow and incorporate business rules.
- Test: Run the bot in a safe environment to validate accuracy and performance.
- Deploy and orchestrate: Move the bot into production, schedule execution, and assign workloads.
- Monitor and optimize: Track performance, resolve exceptions, and refine the workflow.
Once in place, RPA automation can run unattended in the background or in an assisted mode, where bots support employees by taking over parts of their on‑screen work.
Key Business Benefits of RPA Automation
Organizations pursue RPA automation for clear, measurable benefits. When you align initiatives with business priorities, RPA quickly becomes a value generator rather than just a technology project.
1. Cost Savings and Operational Efficiency
- Lower cost per transaction: Bots handle routine tasks at a fraction of the cost of manual work.
- Extended operating hours: RPA can run 24/7, clearing backlogs and supporting round‑the‑clock operations.
- Higher throughput: Automated processes complete more transactions in less time, without overtime.
The result is a leaner, more efficient operation that can do more with the same or fewer resources.
2. Accuracy and Compliance
- Reduced human error: Bots execute the same steps every time, following predefined rules exactly.
- Consistent documentation: RPA can log every action, creating detailed audit trails.
- Improved compliance: Policies and regulatory rules can be embedded directly into bot logic.
This consistency is especially valuable in regulated industries such as financial services, healthcare, and insurance, where data quality and traceability are essential.
3. Better Employee Experience
- Removal of repetitive tasks: Employees spend less time on copying data, filling forms, and reconciling records.
- Focus on value‑adding work: People can concentrate on customer interactions, analysis, and innovation.
- Reduced burnout: Automating high‑volume, monotonous work supports engagement and retention.
By repositioning automation as adigital assistantrather than a replacement, organizations often see higher morale and greater support for transformation initiatives.
4. Faster Customer Response
- Shorter processing times: Approvals, verifications, and data checks happen in minutes instead of days.
- Quicker onboarding: New customers, vendors, or employees can be set up rapidly across multiple systems.
- More reliable information: Clean, up‑to‑date data leads to smoother customer interactions.
Faster, more accurate processing shows up directly in customer satisfaction scores and loyalty.
5. Scalability and Business Agility
- On‑demand scaling: You can add more bots during peak periods and scale back later, without hiring waves of temporary staff.
- Rapid deployment: New automations can be designed, tested, and rolled out faster than traditional system changes.
- Adaptability: As processes evolve, bots can be updated more easily than rigid, hard‑coded integrations.
RPA automation helps organizations respond quickly to market shifts, new regulations, and changing customer expectations.
Best RPA Automation Use Cases by Business Function
RPA can be applied across many departments. Below is a high‑level view of where organizations often see strong returns.
|
Function |
Example Processes |
Primary Benefits |
|
Finance and Accounting |
Invoice processing, accounts payable, reconciliations, expense validation, reporting |
Faster closing, reduced errors, improved cash flow visibility |
|
Human Resources |
Employee onboarding, offboarding, payroll checks, benefits enrollment, data updates |
Better employee experience, accurate records, lower admin workload |
|
Customer Service |
Case routing, status updates, information lookups, order adjustments |
Quicker response, improved first‑contact resolution, consistent service |
|
IT and Operations |
Password resets, user provisioning, batch processing, system health checks |
Reduced tickets, faster resolutions, standardized procedures |
|
Sales and Marketing |
Lead enrichment, data cleansing, report generation, contract data entry |
Cleaner pipelines, better insights, more selling time |
|
Supply Chain and Logistics |
Order processing, shipment updates, inventory reconciliation, vendor data management |
Higher accuracy, fewer delays, improved partner collaboration |
These examples are starting points. Once an organization experiences the impact of RPA automation in one area, it often expands to adjacent processes and departments.
RPA vs Traditional Automation vs AI
RPA automation often gets mentioned alongside traditional automation and artificial intelligence. Understanding the differences helps you choose the right tool for each problem.
RPA Automation
- Imitates human actions on existing interfaces, without changing underlying systems.
- Follows rules and structured workflows.
- Ideal for stable, repeatable processes and system gaps.
Traditional Automation
- Relies on system integrations, custom code, or configuration inside core applications.
- Best for high‑volume processes that are central to a system and unlikely to change often.
- Typically requires more development resources and longer project timelines.
Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Capabilities
- Uses techniques such as machine learning or natural language processing.
- Handles unstructured data, predictions, classification, and pattern recognition.
- Can complement RPA by making decisions that feed into automated workflows.
Many modern solutions combine these elements, usingRPA automationfor process execution and AI for smart decision making, document understanding, and advanced analytics.
Getting Started With RPA Automation
A structured approach makes it easier to launch RPA initiatives that deliver visible results and build momentum.
Step 1: Align With Business Objectives
Start by clarifying what you want RPA automation to achieve. Common goals include:
- Reducing operating costs.
- Improving processing speed.
- Raising accuracy and compliance.
- Freeing capacity for growth without proportional hiring.
When your objectives are clear, it becomes easier to prioritize processes and measure success.
Step 2: Select the Right Pilot Processes
Choose processes that are:
- Stable: Well‑defined and not undergoing major change.
- Manageable in scope: Not too complex for an initial project.
- Impactful: Significant enough that stakeholders will notice improvements.
Good early candidates include invoice processing, data entry, report generation, or standard employee onboarding steps.
Step 3: Map and Standardize the Process
Before building bots, document the current state in detail. Clarify:
- All inputs and outputs.
- Decision rules and edge cases.
- Exceptions and escalation paths.
- Systems and screens involved.
Use this as a chance to simplify and standardize. Automating a poor‑quality process only accelerates its weaknesses.
Step 4: Build, Test, and Iterate
Work jointly with process owners, business analysts, and RPA developers to configure the bot. Involve end users in testing, so you can refine the automation until it behaves as expected across a wide range of scenarios.
Step 5: Deploy and Communicate
Once the bot is ready for production, plan a clear rollout:
- Set expectations about what is changing and what remains the same.
- Explain how the bot supports employees rather than replacing them.
- Share early wins, metrics, and feedback to build enthusiasm.
Communication is often as important as the technology itself in driving adoption.
Building a Strong Business Case for RPA Automation
A compelling business case helps secure sponsorship and investment. Focus on quantifiable benefits and strategic impact.
Identify Baseline Metrics
For each candidate process, capture current performance, for example:
- Average handling time per transaction.
- Number of transactions per period.
- Error rates and rework effort.
- Staff hours required and associated costs.
These baselines allow you to estimate potential improvements with RPA automation.
Quantify Potential Benefits
Model scenarios such as:
- Percentage reduction in manual effort per transaction.
- Expected decrease in errors and related costs.
- Faster processing times and impact on customer experience.
- Avoided hiring costs as volumes grow.
Even conservative estimates often show meaningful returns when processes are good candidates for automation.
Factor in Intangible and Strategic Gains
Not all value is purely financial. Highlight benefits such as:
- Improved employee satisfaction and retention.
- Enhanced compliance, auditability, and risk management.
- Greater agility to respond to market changes.
- A scalable digital workforce foundation for future innovation.
These strategic advantages make RPA automation attractive to leadership teams focused on long‑term competitiveness.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful organizations treat RPA automation as a disciplined, cross‑functional initiative, not just a local technology experiment.
Establish Governance and Ownership
- Create clear roles for decision making, development, and support.
- Define standards for process selection, design, security, and documentation.
- Set up change management procedures to control updates to live automations.
Many enterprises form a dedicated RPA or automation team, often called a center of excellence, to coordinate effort and share best practices.
Prioritize Security and Compliance
- Ensure bots follow the same access controls and approvals as human users.
- Store credentials securely and rotate them according to policy.
- Log bot activities for monitoring and audits.
By embedding security and compliance from the start, you reduce risks and increase trust in automation outcomes.
Design for Exceptions and Human Collaboration
- Plan how bots will hand off complex or ambiguous cases to people.
- Create clear queues or alerts for exceptions that need human review.
- Enable feedback loops so users can flag recurring issues or improvement ideas.
This collaborative design ensures that automation amplifies human strengths rather than operating in isolation.
Start Small, Then Scale
- Begin with a manageable scope where you can deliver value quickly.
- Use early projects to refine your methods and governance model.
- Expand to more complex and cross‑functional processes as your capabilities grow.
A phased approach builds a sustainable automation program that continues to create value year after year.
Measuring Success and Optimizing Over Time
To keep stakeholders engaged, track performance and continuously improve your automations.
Key Performance Indicators for RPA Automation
- Automation coverage: Percentage of process volume handled by bots.
- Time savings: Hours of manual work eliminated or redeployed.
- Error reduction: Decrease in defects, rework, or compliance incidents.
- Cycle time: Reduction in end‑to‑end processing time.
- Return on investment: Benefits compared with implementation and operating costs.
Continuous Improvement Practices
- Review logs and exception reports regularly to identify patterns.
- Consult end users for feedback on handoffs and process bottlenecks.
- Update automations when upstream systems or business rules change.
- Retire or redesign bots that no longer align with current priorities.
Viewing RPA automation as an ongoing capability, rather than a one‑time project, keeps performance aligned with evolving business needs.
Common Myths About RPA Automation
As with any popular technology, myths can create resistance or unrealistic expectations. Addressing them openly helps build support.
Myth 1: RPA Automation Replaces Human Workers
Reality: In most organizations, RPA is used toaugmentstaff, not replace them. Bots take over repetitive tasks, while people move into roles requiring empathy, judgment, and creativity. Many businesses use RPA automation to support growth without continuously expanding headcount.
Myth 2: RPA Works Only for Simple Processes
Reality: While RPA started with straightforward tasks, it has evolved. Combined with business rules and, where appropriate, AI capabilities, it can handle multi‑step workflows with branches and exceptions. The key is to design automations thoughtfully and maintain them over time.
Myth 3: RPA Automation Is a Quick Fix for Broken Processes
Reality: RPA amplifies whatever process it automates. If the underlying workflow is inefficient or poorly designed, automation will replicate those issues faster. Successful organizations use RPA as part of broader process improvement efforts.
The Future of RPA Automation
RPA continues to evolve and expand its role in digital transformation. Several trends are shaping the next wave of innovation.
Convergence of RPA, AI, and Process Intelligence
RPA platforms increasingly include capabilities such as document understanding, machine learning, and process mining. This convergence enables:
- Automation of processes involving unstructured content, such as emails or scanned documents.
- Smarter routing and decision making based on predictive models.
- Automatic discovery of process variations and optimization opportunities.
The result is more powerful, end‑to‑end automation that can adapt as conditions change.
Citizen Development and Business‑Led Automation
Low‑code and no‑code tools are making it easier for business users to participate in building automations under appropriate governance. This trend can:
- Accelerate innovation by tapping into front‑line knowledge.
- Reduce development bottlenecks in central IT teams.
- Encourage a culture of continuous improvement across the organization.
With the right guardrails, citizen development helps organizations scale RPA automation safely and effectively.
From Task Automation to End‑to‑End Journeys
Early projects often target individual tasks. Over time, leading organizations connect multiple automations into cohesive journeys, such as:
- End‑to‑end order‑to‑cash.
- Procure‑to‑pay.
- Hire‑to‑retire in HR.
This shift unlocks larger gains in speed, consistency, and customer experience.
Bringing It All Together
RPA automationoffers a practical, high‑impact path to streamline operations, empower employees, and improve customer outcomes. By focusing on the right processes, aligning with business goals, and building strong governance, you can create a digital workforce that scales with your ambitions.
Whether your priority is cutting manual effort, reducing errors, speeding up service, or supporting growth, RPA can become a central pillar of your automation strategy and a powerful catalyst for continuous improvement.
